How To Remotely Access Raspberry Pi For RemoteIoT: The Ultimate Tutorial
Ever wondered how to remotely access Raspberry Pi for RemoteIoT projects? Well, buckle up because we’re diving deep into this tech-savvy world! Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, remote access to your Raspberry Pi can revolutionize the way you manage IoT systems. In this guide, we’ll explore everything from setting up your Pi for remote access to troubleshooting common issues. Let’s get started, shall we?
Picture this: you’ve built an incredible IoT setup with your Raspberry Pi, but now you’re stuck figuring out how to control it from afar. That’s where remote access comes in. With just a few tweaks and some nifty tools, you can manage your Pi from anywhere in the world. Sounds cool, right? This tutorial isn’t just any guide—it’s your go-to resource for mastering remote Raspberry Pi access.
Before we jump into the nitty-gritty, let’s address the elephant in the room. Remote access isn’t just about convenience; it’s about efficiency and scalability. Whether you’re monitoring sensors, controlling smart home devices, or running complex IoT applications, being able to access your Pi remotely can save you tons of time and effort. So, grab your Pi and let’s make it happen!
Read also:Debbie Depp The Untold Story Of A Hollywood Legacy
Why Remotely Access Raspberry Pi Matters
Now, you might be thinking, “Why should I bother with remote access?” Well, my friend, there are plenty of reasons why this skill is a game-changer. First off, it allows you to monitor and manage your IoT projects without being physically present. Imagine controlling your smart garden system while sipping coffee on the other side of the globe. Pretty neat, huh?
Secondly, remote access enhances productivity. Instead of constantly running back and forth to your Pi, you can troubleshoot issues and tweak settings from the comfort of your couch. Plus, it’s a fantastic way to learn more about networking and security, which are essential skills in today’s digital age.
Lastly, remote access opens up endless possibilities for IoT projects. From home automation to industrial applications, the ability to control your Pi remotely can take your projects to the next level. So, if you’re ready to level up your tech skills, let’s dive into the how-to section!
Understanding the Basics of RemoteIoT
Before we dive into the technicalities, it’s important to understand what RemoteIoT really means. At its core, RemoteIoT refers to the ability to interact with IoT devices from a distance. This includes monitoring data, controlling devices, and troubleshooting issues—all without being physically present.
What Makes Raspberry Pi Ideal for RemoteIoT?
The Raspberry Pi is a tiny but powerful computer that’s perfect for IoT projects. Its low cost, versatility, and ease of use make it a favorite among hobbyists and professionals alike. When it comes to remote access, the Pi shines thanks to its robust networking capabilities and compatibility with various remote access tools.
Read also:Matt Corby Partner The Untold Story Of Love Music And Life
Some key features that make Raspberry Pi ideal for RemoteIoT include:
- Compact size and low power consumption
- Support for multiple operating systems
- Built-in networking capabilities
- Compatibility with SSH, VNC, and other remote access protocols
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Access
Alright, let’s get our hands dirty! Setting up your Raspberry Pi for remote access isn’t as complicated as it sounds. With a few simple steps, you’ll be well on your way to controlling your Pi from anywhere in the world.
Step 1: Install Raspbian OS
The first step is to install Raspbian, the official operating system for Raspberry Pi. You can download the latest version from the official Raspberry Pi website. Once you’ve downloaded the image, use a tool like Etcher to flash it onto an SD card.
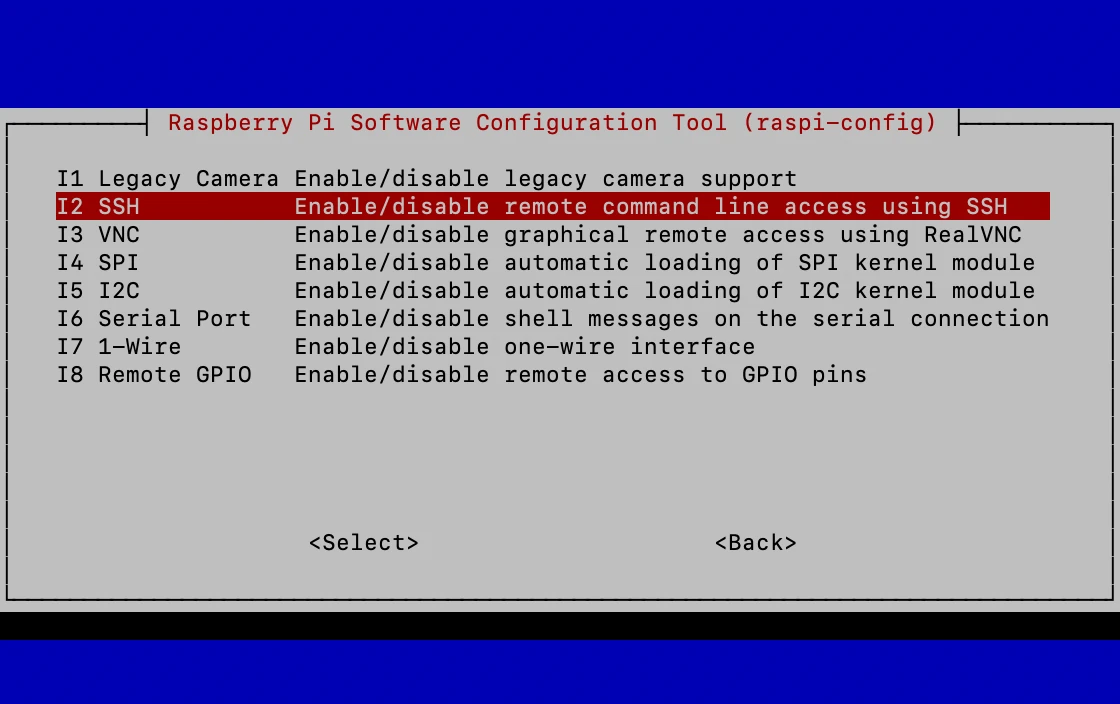
Step 2: Enable SSH
SSH (Secure Shell) is a protocol that allows you to securely connect to your Pi from another device. To enable SSH, simply create an empty file named "ssh" (without any extension) in the boot partition of your SD card. That’s it! SSH will be enabled the next time you boot your Pi.
Step 3: Configure Wi-Fi
If you’re planning to access your Pi wirelessly, you’ll need to configure Wi-Fi. Create a file named "wpa_supplicant.conf" in the boot partition and add your Wi-Fi credentials. This will ensure that your Pi connects to the network automatically on boot.
Using SSH to Remotely Access Raspberry Pi
SSH is one of the most popular methods for remotely accessing Raspberry Pi. It’s secure, reliable, and easy to set up. Here’s how you can use SSH to connect to your Pi:
Step 1: Find Your Pi’s IP Address
To connect to your Pi via SSH, you’ll need to know its IP address. You can find this information by running the "ifconfig" command in the terminal. Alternatively, you can check your router’s admin page for a list of connected devices.
Step 2: Connect Using SSH
Once you have your Pi’s IP address, you can connect to it using an SSH client like PuTTY (for Windows) or the built-in terminal (for macOS and Linux). Simply enter the IP address and log in using your Pi’s credentials.
Step 3: Secure Your SSH Connection
Security is key when it comes to remote access. To protect your Pi, consider changing the default SSH port, using key-based authentication, and setting up a firewall. These steps will help keep unwanted visitors at bay.
Using VNC for Remote Desktop Access
While SSH is great for command-line tasks, sometimes you need a full graphical interface. That’s where VNC (Virtual Network Computing) comes in. VNC allows you to remotely access your Pi’s desktop environment, making it perfect for tasks that require a GUI.
Step 1: Install VNC Server
To use VNC, you’ll first need to install the VNC server on your Pi. You can do this by running the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt-get install realvnc-vnc-server realvnc-vnc-viewer
Step 2: Connect Using a VNC Client
Once the VNC server is installed, you can connect to your Pi using a VNC client like RealVNC Viewer. Simply enter your Pi’s IP address and log in using your credentials. Voilà! You’ll now have full remote desktop access to your Pi.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with the best-laid plans, things can go wrong. Here are some common issues you might encounter when remotely accessing your Raspberry Pi and how to fix them:
- Connection Refused: Double-check your Pi’s IP address and ensure that SSH or VNC is properly configured.
- Authentication Failed: Make sure you’re using the correct username and password. If you’re using key-based authentication, ensure that your keys are correctly set up.
- Network Issues: If you’re unable to connect, check your network settings and ensure that your Pi is connected to the internet.
Security Best Practices for RemoteIoT
When it comes to remote access, security should always be a top priority. Here are some best practices to keep your Raspberry Pi safe:
- Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Regularly update your Pi’s software to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Limit access to trusted devices and IP addresses.
- Monitor your Pi’s activity logs for any suspicious behavior.
Advanced Techniques for RemoteIoT
Once you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to take your skills to the next level. Here are some advanced techniques for remotely accessing your Raspberry Pi:
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding allows you to access your Pi from outside your local network. By configuring your router to forward specific ports to your Pi, you can connect to it from anywhere in the world.
Dynamic DNS
If your internet service provider assigns a dynamic IP address, consider using a Dynamic DNS service. This will give your Pi a fixed domain name, making it easier to connect remotely.
Real-World Applications of RemoteIoT
RemoteIoT isn’t just a theoretical concept—it has real-world applications that can transform the way we live and work. Here are a few examples:
- Smart Home Automation: Control your home’s lighting, temperature, and security systems from anywhere.
- Environmental Monitoring: Use sensors connected to your Pi to monitor air quality, water levels, and other environmental factors.
- Industrial IoT: Manage and monitor industrial equipment remotely, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
Conclusion: Take Your IoT Projects to the Next Level
And there you have it—the ultimate guide to remotely accessing your Raspberry Pi for RemoteIoT projects. From setting up SSH and VNC to implementing advanced security measures, we’ve covered everything you need to know to take your IoT skills to the next level.
So, what are you waiting for? Grab your Pi, follow this tutorial, and start exploring the endless possibilities of RemoteIoT. Don’t forget to share your experiences in the comments below and check out our other articles for more tech tips and tricks. Happy hacking!
Table of Contents
- How to Remotely Access Raspberry Pi for RemoteIoT
- Why Remotely Access Raspberry Pi Matters
- Understanding the Basics of RemoteIoT
- Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Access
- Using SSH to Remotely Access Raspberry Pi
- Using VNC for Remote Desktop Access
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Security Best Practices for RemoteIoT
- Advanced Techniques for RemoteIoT
- Real-World Applications of RemoteIoT